Bitcoin Mining Work Legality Cryptocurrency BTC
Discovering the legality surrounding the fascinating world of blockchain activities has become an indispensable task in today’s evolving financial landscape. As new digital currencies continue to emerge, it is essential to delve into the realm of cryptocurrency mining to shed light on its legality and the regulatory frameworks governing this innovative industry.
Exploring the inner workings of the digital ecosystem, we delve into the art of harnessing the potential rewards of decentralized networks through resource-intensive computational processes. This ambitious endeavor encompasses the generation of new digital assets through a series of complex mathematical algorithms that underpin the very fabric of virtual currencies.
Unveiling the legal landscape of this dynamic sector involves navigating a tapestry of global regulations, governmental policies, and judicial interpretations. The quest to ascertain the legitimacy of Bitcoin and other blockchain-based activities leads us into a multi-faceted realm where robust arguments arise from both proponents and skeptics of this disruptive technology.
Examining the convoluted legal status of cryptocurrency mining presents an avenue to explore the diverse array of regulations imposed by countries worldwide. From nations embracing the innovative potential of blockchain technologies to those expressing concerns over money laundering and illicit activities, the legal framework surrounding cryptocurrency mining displays a fascinating tapestry of approaches and perspectives.
Immersing ourselves in this captivating field, we embark on a journey to gather a comprehensive understanding of the intricate legal landscape within which cryptocurrency mining exists. Delving into specific regions, we explore the legal frameworks, regulations, and enforcement strategies employed to govern the energy-intensive processes involved in generating digital currency units.
Stepping beyond the surface, this article uncovers the nuanced perspectives surrounding the legality of cryptocurrency mining and challenges conventional notions of traditional financial ecosystems. By shedding light on the ever-evolving nature of regulations and the legal implications surrounding mining operations, we aim to unravel the complexity inherent in this cutting-edge industry.
Is Bitcoin Mining Legal?
Exploring the Legitimacy of Bitcoin Mining.
Understanding the Validity
Delving into the realm of cryptocurrency, there is a pertinent question that arises – Is Bitcoin Mining in accordance with the law? Understanding the legal standing of Bitcoin Mining is crucial, as it sheds light on the regulatory framework surrounding this innovative activity. This section aims to delve into the subject matter and explore the legality of Bitcoin Mining.
Unraveling the Legitimacy
When it comes to Bitcoin Mining, one needs to comprehend its legitimacy within the legal sphere. The recognition of Bitcoin Mining as a lawful activity varies across different jurisdictions. Some countries have embraced it, deeming it legal and subject to specific regulations, while others have imposed restrictions or even outright bans. Seeking a clear understanding of the legal landscape surrounding Bitcoin Mining is imperative for those engaging in this practice.
In certain jurisdictions, Bitcoin Mining is seen as a legitimate activity given that it operates within the confines of existing regulations and adheres to specific guidelines. Proponents argue that as long as miners comply with the established legal requirements, they can participate in Bitcoin Mining without any legal concerns.
On the other hand, some countries view Bitcoin Mining as a controversial and potentially illicit activity. Concerns regarding electricity consumption, environmental impact, and potential risks associated with the anonymity of transactions have prompted certain nations to either impose strict regulations or completely ban Bitcoin Mining. It is important for individuals involved in Bitcoin Mining to be aware of the legal stance of their respective countries to avoid any legal consequences.
In conclusion
As with any rapidly evolving technology, the legality of Bitcoin Mining continues to be a subject of ongoing debate and varies from one jurisdiction to another. Whether it is deemed legal or not, it is essential for individuals to educate themselves about the legalities and regulations surrounding Bitcoin Mining while considering the potential risks and benefits associated with this dynamic activity.
Understanding Bitcoin Mining
Unlocking the potential of a groundbreaking technology lies at the heart of the concept we are about to explore. This section aims to shed light on the intricate process behind the creation and verification of new digital assets in a decentralized network, showcasing the backbone of the peer-to-peer cryptocurrency ecosystem.
The Essence of Bitcoin Creation:
In the world of cryptocurrencies, a process known as Bitcoin mining gives birth to new digital tokens and ensures the integrity of transactions. It operates as a decentralized system, safeguarded by a network of participants who commit their computational power to validate and secure the network.
Puzzles and Proof-of-Work:
The foundation of Bitcoin mining lies in solving complex mathematical problems, often referred to as cryptographic puzzles. Miners engage in a race against time, utilizing their computational resources to find the solution that will validate a block of transactions. This process, known as proof-of-work, guarantees that transactions are genuine and ensures the scarcity and validity of new Bitcoins.
The Role of Miners:
Miners play a critical role in both creating and maintaining the Bitcoin network. By dedicating their computational power, they compete to add new blocks to the blockchain, effectively securing the network from fraudulent activities. Successful miners are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins and transaction fees, empowering them to continue their efforts in maintaining the integrity and security of the network.
The Power of Consensus:
Bitcoin mining relies on a consensus mechanism that ensures the decentralized nature of the network. Consensus is achieved through the majority of miners agreeing on which blocks are valid and can be added to the blockchain. This consensus mechanism not only guarantees the authenticity of the network but also inhibits the possibility of a single entity gaining control, making Bitcoin resistant to censorship and manipulation.
Evolving Challenges:
As the popularity and value of Bitcoin continue to grow, mining faces new challenges. The increasing mining difficulty and the dependency on specialized hardware create barriers to entry for individual miners. Additionally, the energy consumption associated with mining has raised concerns regarding its environmental impact. However, innovative solutions and advancements in technology aim to address these challenges and ensure the sustainability and inclusivity of Bitcoin mining.
Conclusion:
Understanding the intricacies of Bitcoin mining allows individuals to grasp the fundamental aspects of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. By comprehending the mechanics behind the creation and security of digital assets, one can further explore the legal implications and surrounding regulations of the Bitcoin mining industry.
The Legal Status of Bitcoin Mining
Exploring the legality surrounding the process of generating new digital assets in the realm of decentralized cryptocurrencies.
As technology continues to evolve, so does the landscape of the financial world. Bitcoin mining, one of the fundamental components of the decentralized cryptocurrency network, has garnered significant attention in recent years. However, when it comes to the legality of this process, opinions and regulations vary across jurisdictions.
Across the globe, governments and regulatory bodies have adopted different approaches towards the legal status of bitcoin mining. Some countries embrace and regulate it within their existing financial laws, recognizing it as a legitimate activity that contributes to the economy. Others, however, maintain a cautious stance due to concerns surrounding financial stability, energy consumption, or the potential for illicit activities.
While some nations have embraced bitcoin mining as a legal and regulated practice, others have adopted a more conservative approach, with varying degrees of prohibition or restrictions. The legal landscape is constantly evolving, with governments adapting their policies to navigate the complexities and potential risks associated with cryptocurrency mining.
It is essential for individuals and businesses involved in bitcoin mining to stay informed about the legal status of the practice within their respective jurisdictions. Understanding the specific legal requirements, permits, and licenses necessary for compliant operations is crucial to avoid legal complications and ensure a sustainable and legitimate approach to mining activities.
Ultimately, the legal status of bitcoin mining is a multifaceted topic, influenced by various factors such as government regulations, energy policies, and evolving legal frameworks. As the world continues to grapple with the opportunities and challenges presented by cryptocurrencies, the legality of bitcoin mining remains a subject of ongoing discussion and adaptation.
Regulations and Licensing
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital currencies, it is crucial to understand the legal framework and licensing requirements surrounding the activities related to the decentralized financial systems. Governments and regulatory bodies across the globe have started to address the intricacies involved in the usage and trading of these digital assets, devising regulations to ensure fair practices and protect investors.
Global Regulatory Trends
- International regulatory bodies are actively engaged in discussions to define the legal status of digital currencies and establish guidelines for their usage.
- Various countries have taken different approaches to regulate digital currencies, spanning from outright bans to establishing specific licensing frameworks.
- Regulatory authorities are concerned about potential risks associated with illegal activities, such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and tax evasion, which can be facilitated through cryptocurrencies.
- Global efforts are being made to develop a unified regulatory approach to ensure consistent and transparent regulations across jurisdictions.
Licensing Requirements
When it comes to licensing requirements for activities related to digital currencies, countries have implemented different frameworks tailored to their respective legal systems. These licenses aim to bring businesses under proper supervision, ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) regulations.
- Some countries require specific licenses for cryptocurrency exchanges, wallet providers, and other intermediaries involved in the trading and storage of digital currencies.
- Regulations may also mandate the registration of entities engaging in initial coin offerings (ICOs) or token sales to protect investors from fraudulent schemes.
- Financial supervision authorities play a crucial role in the licensing process by evaluating the credibility, security measures, and financial stability of the entities seeking licenses.
- Ongoing monitoring and compliance reporting are often mandatory for licensed entities to ensure adherence to the prescribed regulatory requirements.
It is important for individuals and businesses operating in the digital currency ecosystem to stay abreast of evolving regulations and licensing requirements in their jurisdictions. Adhering to these frameworks and obtaining the necessary licenses can help foster a secure and transparent environment for the usage and trading of digital assets.
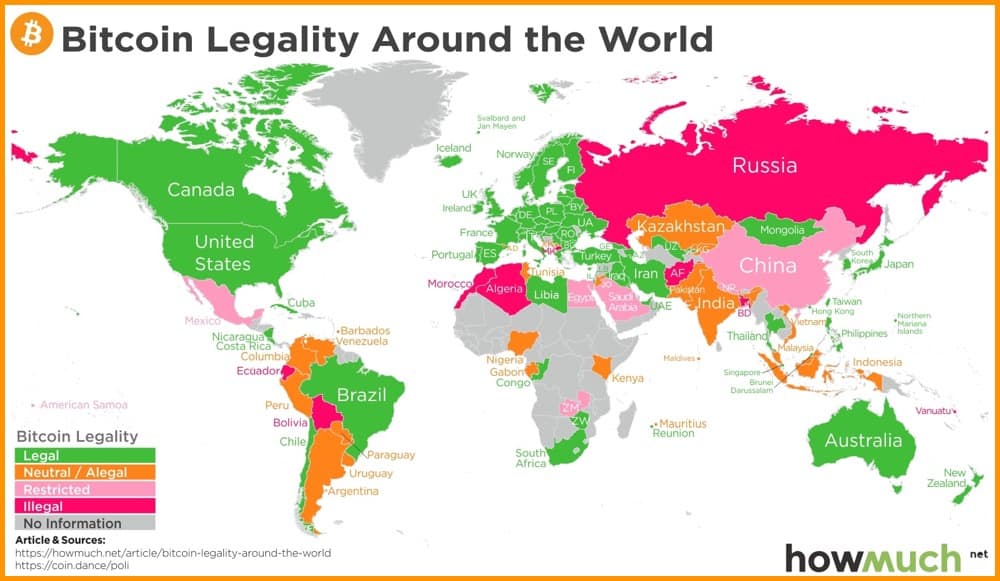
Country-specific Regulations on Bitcoin Mining
Each nation has established its own set of regulations surrounding the process of generating digital currencies through cryptographic algorithms. These laws determine the acceptability, legality, and tax implications of engaging in such activities within their respective jurisdictions. In this section, we will explore the different country-specific laws and regulations governing the practice of creating digital currencies through cryptographic algorithms.
United States
In the United States, the legality of Bitcoin mining varies depending on individual states and their specific regulations. While some states fully embrace and regulate cryptocurrency mining, others may have restrictions or require specific licenses or permits to engage in such activities. It is important for miners to familiarize themselves with the regulations in their respective states to ensure compliance.
China
China, being one of the major players in Bitcoin mining, has shown a fluctuating stance on its legality over the years. The government has implemented various measures to regulate and control the industry, including the banning of cryptocurrency exchanges and imposing restrictions on mining activities. However, some regions in China still allow and support Bitcoin mining with specific regulations and licensing requirements.
| COUNTRY | LEGAL STATUS | REGULATORY FRAMEWORK |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Varies by State | State-specific regulations and licensing requirements |
| China | Restricted | Regional regulations and licensing requirements |
Tax Considerations for BTC Miners
When operating in the realm of digital currency, it is crucial for individuals engaged in the validation and verification process to be well-versed in the tax implications associated with their activities. Awareness and adherence to tax regulations can help miners avoid legal complications and ensure compliance with their country’s tax laws.
1. Income tax on mining rewards:
- Miners receive rewards in the form of newly minted crypto coins, which are considered taxable income in many jurisdictions. It is important for miners to report these rewards as income and pay the corresponding income tax.
- Proper record-keeping is essential to accurately report the value of the received coins at the time of mining. Failure to report mining rewards may result in penalties and legal consequences.
2. Self-employment tax:
- In some countries, mining operations may be classified as self-employment, subjecting miners to self-employment tax rather than traditional income tax.
- Miners should consult with tax professionals or authorities to determine whether they are required to pay self-employment tax and how to calculate and report it correctly.
3. Expenses and deductions:
- Miners may be eligible to deduct certain expenses related to their mining activities, such as electricity costs, mining hardware purchases, and maintenance expenses.
- Keeping detailed records of all expenses is crucial for substantiating deductions and minimizing tax liability.
4. Fair market value reporting:
- If miners exchange their mined cryptocurrency for fiat currency or other assets, they may need to report the fair market value of the crypto at the time of the transaction for tax purposes.
- Consulting with tax professionals can provide guidance on the proper valuation methods and reporting requirements.
5. Capital gains tax:
- If miners hold their mined cryptocurrency as an investment and later sell or exchange it, they might be liable to pay capital gains tax on the resulting profit.
- Understanding the capital gains tax rules and regulations in their jurisdiction is crucial to ensure compliance and calculate the correct tax liability.
It is important for Bitcoin miners to stay updated on the evolving tax regulations and consult with tax professionals to ensure compliance and minimize tax obligations. Due to the complex and ever-changing nature of tax laws, seeking professional advice can help miners navigate the legal landscape and make informed decisions.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes in Bitcoin Mining Regulations
The future outlook and potential changes in regulations related to the process of generating digital currencies through computational power and ensuring their compliance with the law indicate an evolving landscape. As governments worldwide seek to address the complexities surrounding this decentralized technology, various jurisdictions are reevaluating their approaches towards the regulation, supervision, and taxation of these innovative activities.
Moving forward, it is anticipated that there will be an increased focus on establishing comprehensive legal frameworks that strike a balance between promoting innovation and safeguarding the interests of various stakeholders. Authorities are likely to explore potential revisions in existing legislation or the introduction of new regulations, which may impact the way bitcoin mining operations are conducted and regulated.
One potential area of reform in the future could be the adoption of clearer definitions and categorizations for different activities within the bitcoin mining industry. This could help distinguish between various forms of mining, such as individual mining, mining as part of a pool, or mining conducted by large-scale operations. By providing specific guidelines and criteria, authorities can enhance transparency, minimize ambiguity, and facilitate more effective regulatory oversight.
Moreover, as concerns about energy consumption and environmental impact associated with bitcoin mining continue to rise, jurisdictions might reevaluate their energy policies and incentivize the use of sustainable energy sources. This could lead to the introduction of new regulations or the revision of existing ones to encourage more eco-friendly mining practices.
In addition, the international nature of bitcoin mining necessitates collaboration and coordination between governments to prevent regulatory arbitrage and ensure a level playing field. Future developments may witness increased cooperation among authorities globally, including sharing best practices, establishing common standards, and facilitating cross-border enforcement mechanisms to address potential regulatory challenges.
Overall, the future outlook for bitcoin mining regulations presents an opportunity for governments and industry participants to navigate the evolving landscape and create a conducive environment for innovation while protecting against potential risks. The ongoing dialogue and potential changes indicate a willingness to adapt regulations to better align with the dynamic nature of this rapidly expanding sector.
Question-answer: Is bitcoin mining legal
What is the primary purpose of crypto mining in the blockchain ecosystem?
Crypto mining is the process by which transactions are verified and added to the blockchain ledger while also releasing new cryptocurrency coins into circulation.
How do miners typically mine Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies?
Miners use specialized hardware and software to solve complex mathematical puzzles, validating transactions and securing the network in exchange for rewards.
What role does a mining pool play in the crypto mining process?
A mining pool allows multiple miners to combine their computational resources to increase the chances of successfully mining a block and earning rewards, which are then distributed among pool participants.
What is the significance of the term “hash” in the context of crypto mining?
A hash is a cryptographic function used in the mining process to create a unique identifier for each block of transactions, ensuring the integrity and security of the blockchain.
How is the block reward in crypto mining typically determined?
The block reward refers to the number of new cryptocurrency coins released to miners for successfully mining a block, with Bitcoin currently rewarding miners with 6.25 BTC per block.
What type of equipment is commonly used in crypto mining operations?
Miners often use specialized hardware such as application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) or graphics processing units (GPUs) to perform the computational tasks required for mining.
What is the significance of the term “hash rate” in crypto mining?
The hash rate represents the computational power or speed at which a mining device or network can perform cryptographic calculations, often measured in hashes per second (H/s).
How does the mining process change every four years in the Bitcoin network?
Every four years, the block reward issued to miners is halved in an event known as the mining compute equipment “halving,” reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are created and affecting bitcoin block the incentives for miners.
What distinguishes an ASIC from other types of mining hardware?
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is a specialized piece of hardware designed specifically for mining a particular cryptocurrency, offering significantly higher efficiency and performance compared to general-purpose hardware like GPUs.
How does the mining process contribute to the security and decentralization of blockchain networks?
Mining involves the computational effort required to validate and secure transactions on a blockchain, with miners competing to add new blocks to the chain. This process ensures consensus and prevents malicious attacks, thus maintaining the integrity and decentralization of the network.
How does one typically join a mining pool for Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies?
To join a mining pool, miners usually need to register an account with the pool and configure their mining software to connect to the pool’s mining servers.
Is Bitcoin mining legal in most jurisdictions?
Yes, Bitcoin mining is generally legal in most jurisdictions, although regulations and policies regarding cryptocurrency mining may vary from country to country.
Who are crypto miners, and what is their primary role in the Bitcoin network?
Crypto miners are individuals or entities that use computational power to validate transactions and secure the network by solving complex mathematical puzzles in exchange for rewards.
What factors contribute to the profitability of Bitcoin mining?
The profitability of Bitcoin mining depends on several factors, including the price of Bitcoin, the cost of electricity, the efficiency of mining hardware, and the difficulty of mining.
How often does the Bitcoin network undergo a “halving” event, and what is its significance?
The Bitcoin network experiences a halving event approximately every four years, reducing the block reward issued to miners by half. This event impacts the rate of new Bitcoin creation and influences mining economics.
What types of hardware are commonly used in Bitcoin mining rigs?
Bitcoin miners often use specialized hardware called ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) designed specifically for mining Bitcoin efficiently.
What role does proof of work play in the Bitcoin mining process?
Proof of work is a consensus mechanism used in Bitcoin mining, requiring miners to demonstrate computational effort to validate transactions and create new blocks on the blockchain.
How frequently are new Bitcoins mined, and what is the current reward for mining a block?
Approximately every 10 minutes, a new block of Bitcoin transactions is mined, with miners currently rewarded 6.25 Bitcoins per block.
Can mining pools increase the profitability of Bitcoin mining for individual miners?
Yes, joining a mining pool allows miners to combine their computational resources, increasing their chances of successfully mining blocks and earning rewards, which are then distributed among pool participants.
Are there any risks associated with Bitcoin mining, particularly for mining firms or operations?
Yes, Bitcoin mining carries risks such as fluctuating cryptocurrency prices, regulatory uncertainties, hardware obsolescence, and operational costs, which can impact profitability and sustainability.